GPS Follow and Image Follow are advanced tracking features that allow drones to autonomously follow a target, enhancing usability for aerial photography, sports tracking, and other applications.
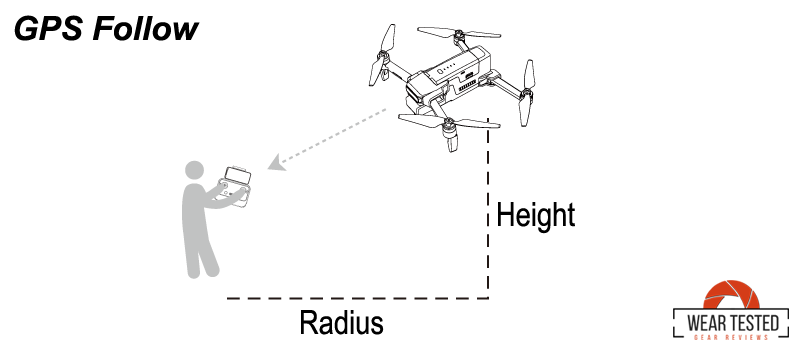
GPS Follow uses the drone’s GPS system and, often, a GPS signal from a connected mobile device or a remote controller to track and follow the user.
Here’s how it works:
- GPS Synchronization: The drone receives GPS location data from the target device (e.g., a smartphone) carried by the user.
- Automatic Tracking: Using this GPS data, the drone continuously adjusts its flight path to maintain a consistent distance and angle from the target.
- Advantages:
- GPS follow mode is dependable over long distances and can be effective in open spaces.
- The drone doesn’t rely on visual input so obstacles like trees and other objects won’t obscure it tracking the user.
- Limitations:
- Accuracy may vary based on GPS signal strength, and it can struggle with precise positioning in densely built-up or indoor areas.
GPS Follow Mode is more suited for broader, straightforward tracking over longer distances and doesn’t require visual contact with the subject, but it may face limitations in obstacle avoidance and signal issues.
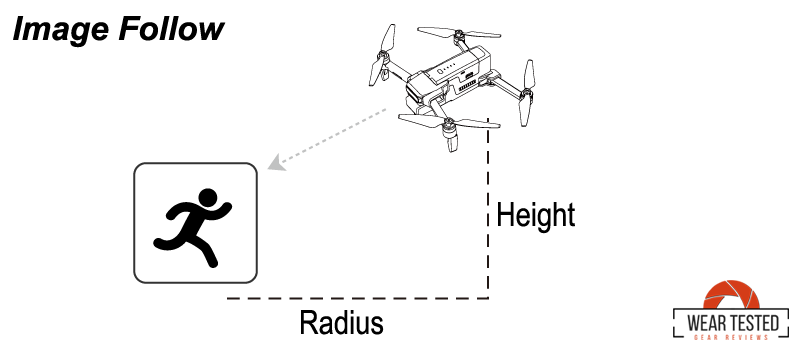
Image Follow, often referred to as visual tracking or object recognition follow, relies on the drone’s camera and onboard image processing technology to visually track the target.
Here’s how it works:
- Visual Identification: The drone’s software identifies and locks onto a target within the video feed, such as a person or a specific object.
- Real-Time Tracking: Using AI and machine learning algorithms, the drone keeps the target centered in the frame by continuously adjusting its position based on movement and orientation.
- Advantages:
- It provides a more accurate tracking experience in terms of alignment and framing since it “sees” the target.
- It is especially useful for capturing complex shots or when GPS is unavailable, such as indoors.
- Limitations:
- Requires good lighting and unobstructed views; tracking can falter if the target moves out of view or behind obstacles.
- May have limited functionality in low-light conditions or if the visual recognition system isn’t advanced.
Image Follow Mode provides more dynamic and visually engaging footage by directly tracking the subject through camera sensors, but it requires clear visibility and good lighting to perform optimally.
For smooth tracking (GPS Follow or Image Follow) videos, use these guidelines.
GPS Follow Mode
- Choose an Open Area: Select a location free of obstacles to ensure the drone can follow the GPS signal without interruption.
- Maintain Altitude: Keep the drone at a height above potential obstacles to prevent collisions.
- Consistent Speed: Move at a steady pace to allow the drone to maintain a stable following distance.
- Strong GPS Signal: Ensure there is a strong GPS connection for accurate tracking.
Image Follow Mode
- Good Lighting Conditions: Use daylight or well-lit environments to enhance the camera’s ability to track the subject.
- Distinct Subject: Ensure the subject stands out from the background to improve recognition accuracy.
- Avoid Quick Movements: Keep movements smooth and steady to prevent losing track of the subject.
- Evaluate Different Modes: Experiment with ActiveTrack modes like Trace and Parallel for varied perspectives.
By following these strategies, you can effectively highlight the capabilities of both GPS and Image Follow features on your drone.